Measuring Information Intake in a Virtual Generation
This learn about explored American citizens’ information intake throughout quite a lot of kinds of assets. Total, this file supplies a way of the way American citizens perceive questions on information intake within the electronic age and alternative ways researchers can measure on-line information conduct. Listed below are some definitions of key phrases used during this file:
- Platform: The medium in which information is fed on. In particular, this file seems to be at tv, radio, print publications, electronic gadgets (smartphones, computer systems or capsules) and quite a lot of on-line assets (information web sites or apps, social media, search engines like google, podcasts and e-mail newsletters).
- Virtual platform: Information platforms that require somebody to make use of electronic era to eat information content material, comparable to a smartphone or information web site.
- Analog platform: Platforms that don’t seem to be electronic, comparable to a tv set, radio or print newspaper.
- Supplier: The kind of information group generating information tales. In particular, this file seems to be at day-to-day newspapers; cable, native and community TV information; and public and communicate radio. (Community TV information comprises nationwide information systems airing at the broadcast networks of ABC, CBS, NBC, and PBS [e.g., World News Tonight].)
- New platforms: A more moderen form of electronic platform that buyers can use to get right of entry to information. In particular, this file seems to be at good audio system, streaming gadgets (comparable to a Roku or Fireplace Stick), smartwatches, push notifications or indicators and web streaming services and products (comparable to Netflix or Hulu).
- Information aggregator: A electronic information platform that collects information content material from present information organizations and gifts them in one location on-line. In particular, this file seems to be at Google Information, Apple Information, Flipboard and Pocket.
- Unique information reporting: The method the place reporters without delay seek the advice of number one assets with the intention to increase information content material. That is outstanding from aggregation of reports from different assets.
- Passive information: Knowledge on contributors’ on-line process, comparable to surfing historical past and hyperlinks clicked on, which used to be accumulated by way of a monitoring device that panelists downloaded to their electronic gadgets, and that mechanically tracked their on-line behaviors.
- Fit/mismatch: After having their electronic process tracked for a time frame, contributors took a survey that requested about their on-line information intake conduct. Researchers then when put next their responses to those survey questions with the contributors’ on-line process as captured within the passive information. A “fit” happened if a panelist stated they were given information a definite collection of instances within the survey and used to be additionally seen getting information that collection of instances of their passive information. A “mismatch” happened if a panelist stated they were given information a definite collection of instances within the survey however used to be seen getting information much less regularly of their passive information.

The inside track media’s transition to electronic has introduced main upheaval to the {industry} – together with a mess of recent suppliers and tactics to get to information. And simply as American information organizations have needed to greatly reevaluate their industry fashions, it will make sense that researchers who’re looking to measure the U.S. public’s information intake additionally want to reexamine the normal tactics they’ve finished so.
Within the mid-Twentieth century, when media analysis got here into its personal, this process used to be easier. There have been just a few alternative ways to get information, and all have been obviously distinct – print publications, radio or tv. However over the last a long time, along with a plethora of recent types of information (from 24-hour information channels to information web sites), many information retailers now not keep confined to generating content material on just one platform. For example, to satisfy the rising electronic target market, newspapers like The New York Instances additionally produce audio podcasts, which can also be heard on radio stations via a sensible speaker, and video sequence, which can also be observed on a cable TV community via a streaming tool (comparable to a Roku or Fireplace Stick). And cable information retailers and different information suppliers have an lively presence on Fb, YouTube and different social media websites, additional blurring the road between platforms. In any case, there may be an industry-wide fear that information intake conduct are puffed up in surveys the place respondents self-report their habits.
Given the expanding complexity and interconnectedness of this information panorama and issues round overreporting of reports intake, Pew Analysis Middle sought after to discover how easiest to measure information intake: The place do these days used survey practices nonetheless paintings and the place may adjustments be so as?
This file is the end result of this effort and is arranged into 3 sections: Bankruptcy 1 seems to be at the U.S. public’s familiarity with more moderen ideas associated with information; Bankruptcy 2 examines imaginable tactics to fortify survey-based measures of reports intake; and Bankruptcy 3 compares survey effects to using passive information that comes directly from monitoring device information shoppers downloaded to their electronic gadgets.
American citizens are in large part conversant in new applied sciences however regularly don’t recall to mind them as information assets
Contents
- 1 American citizens are in large part conversant in new applied sciences however regularly don’t recall to mind them as information assets
- 2 Conceivable tactics to fortify survey questions on information intake
- 3 Knowledge assets and techniques
- 4 American citizens are in large part conversant in new applied sciences however regularly don’t recall to mind them as information assets
- 5 Conceivable tactics to fortify survey questions on information intake
- 6 Knowledge assets and techniques
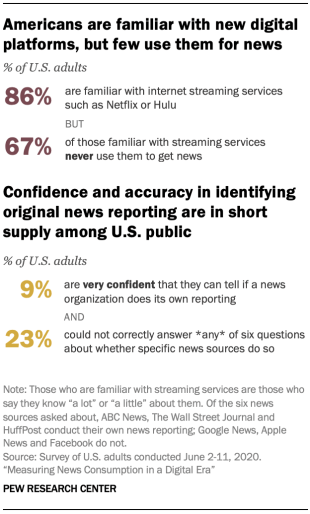
Within the survey of U.S. adults, there may be blended proof in regards to the public’s figuring out of more moderen types of media and information, which has an have an effect on at the subjects survey researchers can moderately ask about. U.S. adults are extensively conversant in applied sciences like streaming gadgets or services and products, podcasts and information indicators. On the similar time, despite the fact that, many don’t appear to make use of these kind of for information intake, and effects from the cognitive interviews counsel that many don’t even assume of those new paperwork as tactics to get information.
Moreover, as information shoppers navigate a knowledge atmosphere that comes with information aggregators and social media feeds, confusion abounds in regards to the authentic supply of reporting. Simplest 9% of U.S. adults are very assured that they may be able to inform if a information group does its personal reporting, and, when requested to spot which of six assets do that (See Bankruptcy 1), just about 1 / 4 (23%) may now not determine any of them appropriately.
In any case, in an period of swiftly converting industry fashions for information organizations, this learn about unearths a necessity for survey researchers to scrupulously specify what they imply by way of “paying for information.” When requested in most cases in the event that they pay for information, many of us don’t appear to think about particular ways in which they do pay for information – to not point out the massive bite of American citizens who not directly pay for information, comparable to via a cable TV subscription.
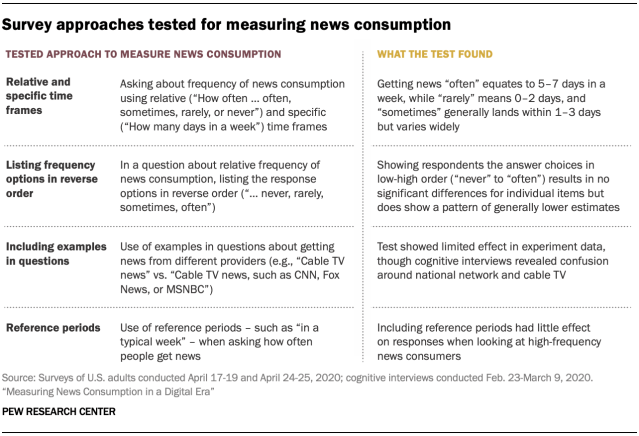
Conceivable tactics to fortify survey questions on information intake
The findings divulge that, whilst there is not any “silver bullet” for highest survey measures of reports intake, a chain of refinements may force marginal enhancements – comparable to across the purpose of decreasing overreporting.
The learn about examined various ideas, together with including a reference duration – e.g., “In the previous week, what number of days did you get information from …” – or examples – e.g., “Day by day newspapers (comparable to The New York Instances, Wall Boulevard Magazine, or your native day-to-day paper)” – to core survey questions on information intake. The learn about discovered that those two adjustments in large part don’t impact estimates of reports intake a number of the U.S. public total, even supposing they will make necessary variations for particular platforms. For example, a selected reference duration seems to get extra correct measures of radio intake, and examples would possibly lend a hand respondents to higher perceive what is supposed by way of nationwide community TV retailers, that have been regularly puzzled with cable TV information in cognitive interviews.
Additionally, the learn about unearths that, when asking about how regularly other folks eat information, appearing the reaction choices in low-to-high order (i.e., beginning with “by no means” and dealing as much as “regularly,” moderately than the opposite) produces no vital variations on particular person pieces however did display a development of in most cases decrease estimates of reports intake. And whilst there’s a shut correspondence between respondents announcing they get information “regularly” or “infrequently” and announcing they achieve this a selected collection of days every week, a reaction of “occasionally” is used to signify a variety of information intake conduct. In different phrases, to 1 respondent, “occasionally” can imply as soon as every week, and to some other, it might imply 3 times every week or extra.
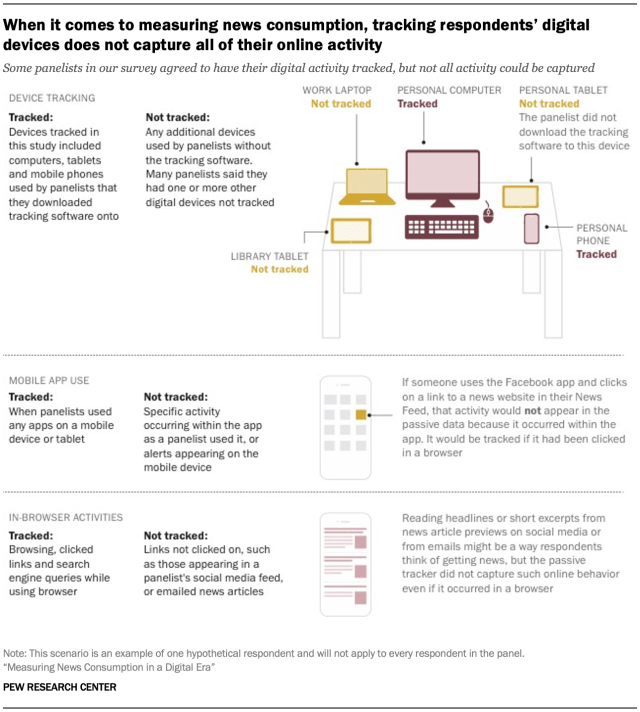
An exploration of the prospective to make use of passive information, received from device other folks obtain to file their actions on-line, as a right away dimension of the general public’s electronic information conduct – freed from the worries with self-reporting inherent to surveys – displays some promise. But there are nonetheless too many pitfalls to depend on it for a whole portrait of American citizens’ electronic information intake. Estimates coming in from passive information are systematically not up to the ones from survey questions, with insufficient protection of gadgets being one obvious wrongdoer: Lots of the respondents who agreed to have their information intake tracked stated that that they had further gadgets that have been now not being tracked, and so a few of their information intake used to be most likely now not captured.
That isn’t the most effective imaginable factor with passive information, which in most cases can not monitor in-app information intake (e.g., when somebody faucets on a hyperlink to a information tale inside a social media app). And a identical dimension from a business metrics supplier is available in even upper than the estimates from the survey information. This issues to 1 power of the survey method: its assets of error are constant, well-studied, and broadly understood, whilst the assets of error in passive information are, at this time, unclear, dependent at the specifics of knowledge assortment, and tough to regulate for.
Survey-based dimension of reports intake isn’t with out its personal issues – in all probability major amongst them is other folks’s tendency to magnify their information intake, consciously or now not. The learn about unearths robust proof of this: Many American citizens say that following the inside track is “crucial” to being a excellent citizen, and people who say this are much more likely than others to overestimate their information intake when their survey responses are when put next with passive information tracked on their gadgets. This means that following the inside track is observed as a “socially fascinating” habits by way of many of us, which would possibly cause them to assume aspirationally about their information intake – i.e., how regularly they preferably intend to eat the inside track moderately than how regularly they if truth be told do – when answering survey questions on it.
Nonetheless, total, this yearlong analysis effort unearths the continuing worth of survey analysis – each in and of itself and when put next with different choices – and signifies tactics to additional fortify information high quality. The power of survey analysis sticks out specifically for the aim of offering complete and related monitoring of the general public’s information intake conduct over the years and taking pictures a consultant slice of the entire U.S. grownup inhabitants in addition to demographic subgroups. Additional, surveys permit the dimension of more than one other types of information intake (now not simply electronic) in the similar manner, on the similar time – and throughout time. Passive information has helpful packages within the client international and could be a device for publishers and others who desire a fine-grained image of consumer habits. However the information does now not, at this time, appear nicely fitted to high-level estimates of reports intake.
It’s value noting that Pew Analysis Middle’s personal organizational experience in survey paintings would possibly incline its researchers towards a extra enthusiastic endorsement of that technique. However the Middle has additionally lengthy explored and produced information intake analysis the usage of different kinds of information assortment, comparable to monitoring the social media conduct of a consultant pattern of U.S. adults, monitoring process in public social media areas round positive subjects, finding out aggregated seek habits round information occasions and making use of industrial metrics. The Middle, in particular within the house of reports analysis, seems to be ahead to proceeding to discover new information alternatives and additional traits of those who have already transform to be had. As we put it on our web site: “We proceed to seek for tactics to amplify and make stronger the normal methodologies that underlie survey analysis and to discover the possibility of change strategies of accomplishing surveys and measuring public opinion.”
Knowledge assets and techniques
This learn about took a multimodal method to investigating those questions, drawing on cognitive interviews, split-form survey experiments, comparisons between passive information and self-reported survey information and a complete, nationally consultant survey. The main points of each and every are supplied in brief underneath.
After an preliminary spherical of brainstorming and checking out, the formal procedure started with cognitive interviews performed amongst 21 respondents via RTI World. The purpose used to be to get qualitative comments at the proposed survey questions and to realize some initial wisdom at the public’s figuring out of rising ideas round information intake in a electronic age. After RTI personnel performed knowledgeable evaluation of the questionnaire, respondents took a draft model of the entire information intake questionnaire and have been probed to speak via their responses, in conjunction with some particular probes asking about their figuring out of key ideas. Those effects are incorporated during the file for added context for some findings.
Survey experiments have been then performed on two separate Ipsos KnowledgePanel surveys in April 2020, with more or less 1,000 respondents in step with survey break up randomly throughout two other paperwork. The purpose used to be to check other approaches to measuring information intake (e.g., part have been requested how regularly they get information on tv, and part have been requested how regularly in an ordinary week they get information on tv) and to decide which model of positive questions would easiest scale back the total occurrence of reported information intake, in mild of study that has recognized doable overreporting of reports intake in surveys. Those effects can basically be present in Bankruptcy 2.
In any case, 3,715 contributors of Ipsos’ KnowledgePanel spoke back to a customized nationwide survey fielded June 2-11, 2020. Roughly part (N=1,694) had up to now consented to have their electronic process tracked on a number of gadgets. This passive information used to be when put next with their self-reported information from the survey. For example, they have been requested in the event that they used the web site or app of The New York Instances prior to now week, and this used to be when put next with the data in their electronic process. As well as, those passively monitored panelists have been when put next with the overall inhabitants pattern to lend a hand perceive the potential of the usage of passive information to measure information intake. Those effects can also be present in Bankruptcy 3.
The remainder 2,021 respondents have been a nationally consultant basic inhabitants pattern of U.S. adults who finished the survey, from which information is principally getting used for basic level estimates and over-time pattern comparisons. Their effects can also be present in Bankruptcy 1. All respondents took the survey on-line. House web get right of entry to used to be supplied to adults who didn’t up to now have it all the way through panel recruitment.
For extra main points, see the technique.


