Social media platforms are necessary for political and social activists. However whilst maximum American citizens consider those platforms are an efficient device for elevating consciousness and growing sustained actions, majorities additionally consider they’re a distraction and lull other people into believing they’re creating a distinction once they’re no longer, in line with a brand new Pew Analysis Heart survey.
General, eight-in-ten American citizens say social media platforms are very (31%) or quite (49%) efficient for elevating public consciousness about political or social problems, in line with the survey of U.S. adults performed July 13-19. A an identical proportion (77%) believes those platforms are a minimum of quite efficient for growing sustained social actions.
Smaller stocks – although nonetheless majorities – say social media are a minimum of quite efficient in getting elected officers to be aware of problems (65%), influencing coverage choices (63%) or converting other people’s minds about political or social problems (58%).
Pew Analysis Heart performed this learn about to know how American citizens consider the effectiveness of social media as a device for social and political activism, alternate and engagement. For this research, we surveyed 10,211 U.S. adults from July 13 to 19, 2020. Everybody who took section is a member of the Heart’s American Traits Panel (ATP), a web based survey panel this is recruited via nationwide, random sampling of residential addresses. This manner just about all U.S. adults have an opportunity of variety. The survey is weighted to be consultant of the U.S. grownup inhabitants via gender, race, ethnicity, partisan association, schooling and different classes. Learn extra in regards to the ATP’s method.
Listed below are the questions used for this document, in conjunction with responses, and its method.
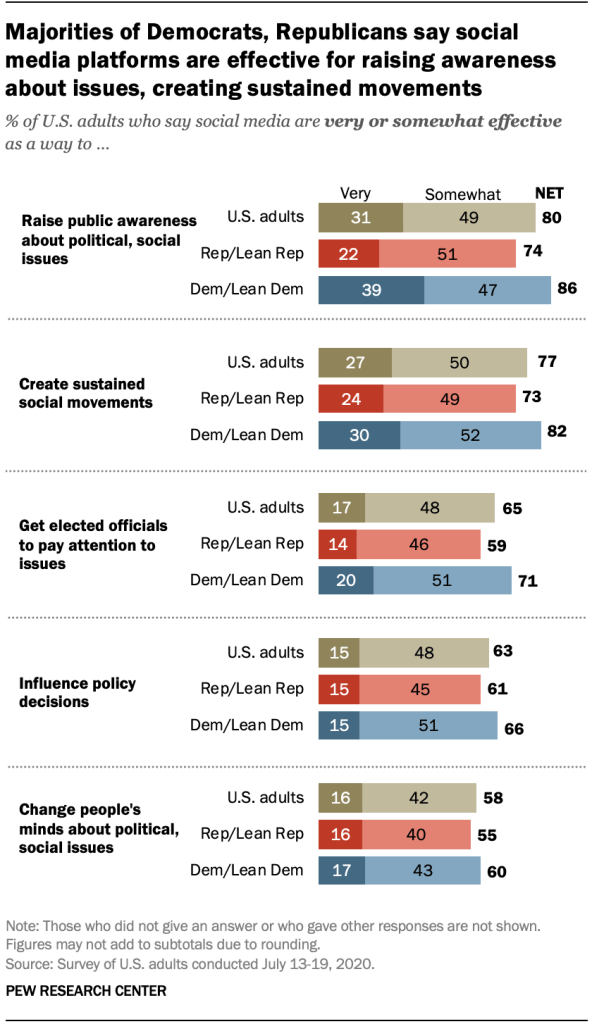
Throughout political events, extra describe those platforms as efficient somewhat than useless in terms of reaching those objectives. Nonetheless, there are some partisan variations.
Democrats and independents who lean Democratic are much more likely than Republicans and Republican leaners to mention social media websites are a minimum of quite efficient so as to elevate public consciousness about political or social problems (86% vs. 74%), create sustained social actions (82% vs. 73%) and get elected officers to be aware of problems (71% vs. 59%). Partisan gaps are extra modest in terms of those platforms’ effectiveness at influencing coverage or converting other people’s minds.
Democrats additionally stand out as seeing social media platforms as very efficient for elevating consciousness: 39% of Democrats say social media are very efficient at this, when compared with 22% of Republicans.
Comparable: 55% of U.S. social media customers say they’re ‘wiped out’ via political posts and discussions
Whilst more youthful American citizens are much more likely than their older opposite numbers to make use of some social media platforms, there are few age-related variations in perspectives of those websites’ effectiveness for political engagement – and birthday party variations persist even amongst more youthful adults for some objectives. As an example, 87% of Democrats ages 18 to 29 say social media websites are a minimum of quite efficient for elevating consciousness, when compared with 76% of Republicans in the similar age workforce. Democrats ages 18 to 29 also are much more likely than their Republican opposite numbers to mention those websites are a minimum of quite efficient at growing sustained social actions (84% vs. 74%) and getting elected officers to be aware of problems (72% vs. 60%).
Main as much as the presidential election, social media platforms have performed a job in elevating consciousness about balloting problems, spreading details about the presidential applicants and permitting customers to have interaction in on-line activism and campaigning. But if requested about social media’s broader affect on political discourse, there are some indicators that American citizens assume those platforms may have each certain and side effects.
At the extra certain aspect, about two-thirds of American citizens say the statements “social media spotlight necessary problems that may no longer get a large number of consideration differently” (65%) and “social media assist give a voice to underrepresented teams” (64%) describe social media very or quite smartly. Part of American citizens additionally say the remark “social media show you how to cling robust other people in control of their movements” describes those platforms a minimum of quite smartly.
However even greater stocks of the general public assume those platforms are distractions and that individuals is also attractive in “slacktivism” – a time period critics have used to explain activism on-line. More or less eight-in-ten American citizens (79%) say the remark “social media distract other people from problems which are in reality necessary” describes social media very or quite smartly, whilst a an identical proportion (76%) say the similar in regards to the remark “social media make other people assume they’re creating a distinction once they in point of fact aren’t.”
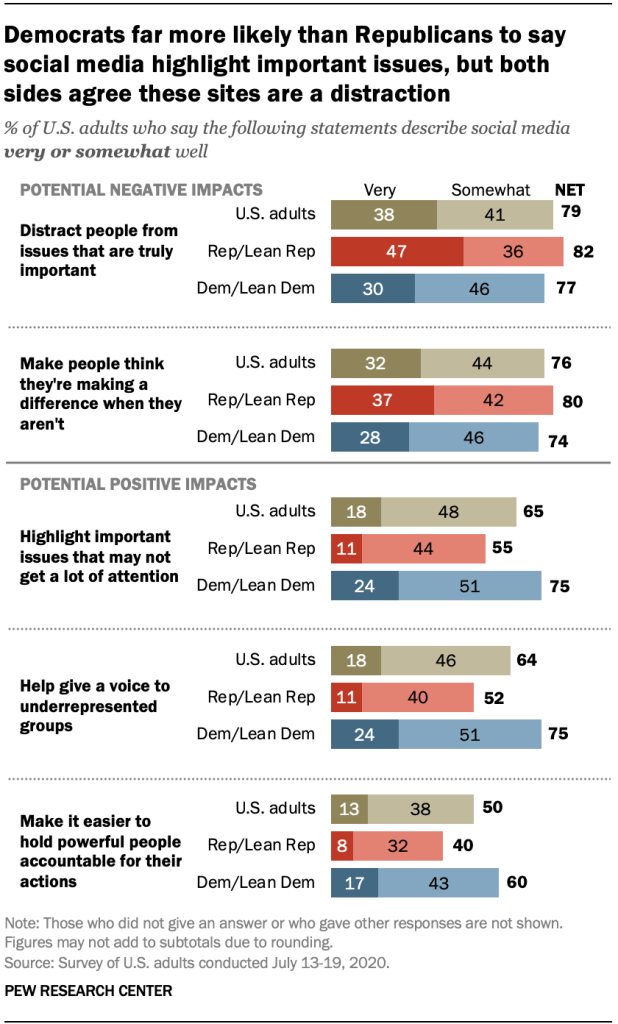
Democrats are much more likely than Republicans to look certain affects of social media. As an example, three-quarters of Democrats say the remark “social media spotlight necessary problems that would possibly not get a large number of consideration differently” describes those platforms a minimum of quite smartly, when compared with 55% of Republicans. Democrats also are much more likely than Republicans to mention those platforms assist give a voice to underrepresented teams (75% vs. 52%) and show you how to cling robust other people in control of their movements (60% vs. 40%).
By way of comparability, there’s extra partisan settlement in terms of some adverse sides of the usage of social media platforms for political engagement. On the other hand, Republicans are a little bit much more likely than Democrats to consider that social media distract other people from problems which are in reality necessary (82% vs. 77%) or make other people assume they’re creating a distinction once they in point of fact aren’t (80% vs. 74%).
More youthful American citizens generally tend to have a extra certain outlook in regards to the societal affect of social media. However as with political engagement, partisan variations nonetheless exist inside the youngest age workforce. As an example, 70% of Democrats ages 18 to 29 say social media show you how to cling robust other people in control of their movements, when compared with 49% of Republicans in the similar age workforce. Younger Democrats also are much more likely than their GOP opposite numbers to mention social media assist give a voice to underrepresented teams (82% vs. 63%) and spotlight necessary problems that may no longer differently get consideration (79% vs. 64%).
American citizens’ perspectives on a few of these problems are statistically unchanged since 2018, the ultimate time the Heart requested those questions. As an example, there was no notable alternate in other people’s perspectives about social media serving to to offer a voice to underrepresented teams, highlighting necessary problems and distracting other people from necessary problems.
Nonetheless, there was modest alternate in terms of the belief that social media show you how to cling robust other people in control of their movements. Part of American citizens now say this, down from 56% in 2018. On the similar time, there was an uptick within the proportion of American citizens who say social media platforms are making other people assume they’re creating a distinction once they in point of fact aren’t, from 71% in 2018 to 76% within the new survey.
A few of these adjustments persist when having a look at partisan association. The proportion of Republicans who say social media show you how to cling robust other people in control of their movements has dropped from 51% in 2018 to 40% as of late, whilst perspectives are unchanged amongst Democrats. In the meantime, Democrats have transform quite much more likely to mention social media make other people assume they’re creating a distinction once they in point of fact aren’t (+7 share issues), whilst Republican perspectives are extra constant throughout years.
Notice: This is a part of a chain of weblog posts main as much as the 2020 presidential election that explores the function of social media in politics as of late. Listed below are the questions used for this document, in conjunction with responses, and its method.

Supply By way of https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2020/09/09/americans-think-social-media-can-help-build-movements-but-can-also-be-a-distraction/


